Best Practices for HTML to WordPress website

Uncover key considerations for converting HTML to WordPress while addressing key factors related to what makes for the best project settings, the process of integration, and site administration.
- Project Settings
If WordPress is going to be based on Gutenberg blocks, the layout build should be without chunks, one app.css file, and one app.js file.
To disable the chunking section, add the following code to webpack.config
new webpack.optimize.LimitChunkCountPlugin({
maxChunks: 1
}),
example:

All JS components must be connected in the JS file responsible for the main page. Most often, this file is js/pages/index.js;
All pages in the layout must have an attribute in the html tag data-template-name=”index”.
- Header
The menu is wrapped with the nav tag. The menu list should contain only links to the relevant sections. It is not allowed to add li elements with any icon or additional element that is not a navigation element (span with the text “all products”, etc.).
The class for the active menu item should be hung on the <li> tag, not on the <a>
- Work with page elements
All H1 – H6 headings, a, p, ul, ol, and blockquote tags must be styled without reference to the element class directly through the tag ( h1 {some style here} ). It is allowed to style through the parent selector, which will be used as a wrapper on the single blog post page
pages like:

For blocks such as tabs, chords, etc. that have id attributes such as id=”tab-0″, id=”tab-1″… Start numbering from 0 (zero).
- Content
It is better to style the content of such blocks by tags from the parent wrapper element rather than by classes. To do this, you will use a WYSIWIG editor rather than breaking it down into a bunch of fields for the title, text, or link. This will make it easier for the user to fill the site with content. This also applies to pages such as Privacy policy, Terms of use.
Some simple decors for the text should be made using the <strong> tag.
The span tag is not allowed in this case. Below, you can see the tags that can be used (plus all h*, p, a)
It is not allowed to use modifier classes with a sequential block number (for example, service_section-1, service-section-2, etc.). In this case, use the css nth-child(n of classname)
Lists with icons, if they are inside a block with text, should be made without additional classes, icons through :before and base64
- Forms
How is the form implemented on WordPress, Contact Form 7, or Gravity Forms?
In the case of Gravity Forms, you first need to create a form on WP and only then style it, because the plugin provides its own markup
for example:
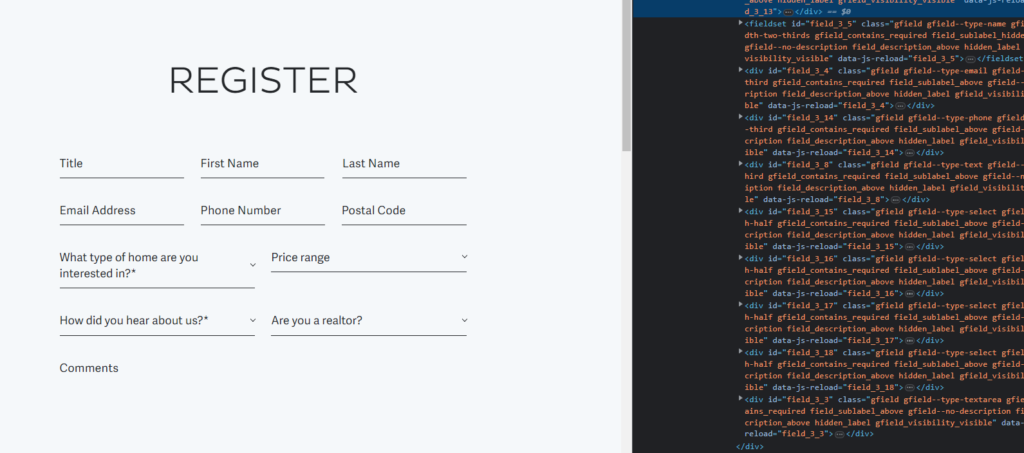
In the case of Contact Form 7, we layout the form as usual.
Drop-down lists (selects) – if there are no requirements for js plugins, use the native select tag or the tom-select plugin.
- Markup of WordPress content elements
The full set of possible elements of the WordPress page and their markup are added to our template, the article.html page.
- Making layout changes after integration into WordPress
If your layout block has already been integrated into WordPress (you can check this by searching the project files), you should make all further changes to the markup in the php template as well.

